Medical updates: More than 58% of all cervical cancer cases worldwide were projected to be in Asia, with India accounting for the greatest number of cases (21%), followed by China (18%). A recent study found that 23% of the 40% of mortality globally from cervical cancer takes place in India, followed by 17% in China.
More than half of deaths were predicted to occur in Asia (58%) before moving on to Africa (22%), Europe (10%), and Latin America (10%), according to the study.
In 2020, there were 3,41,831 deaths worldwide from cervical cancer and an estimated 6,04,127 new cases. According to the data, India recorded about 21% of all cervical cases.
The analysis is based on projections from The Global Cancer Observatory (GLOBOCAN) for 2020, which take into account historical, geographic, and socioeconomic changes.
“More than 58% of all cases of cervical cancer globally were estimated in Asia followed by Africa (20%), Europe (10%) and Latin America (10%) and more than half of deaths were estimated in Asia (58%) followed by Africa (22%), and Latin America (9%). Around 39% of all cases occurred in China (18%) and India (21%) and 40% of total deaths from cervical cancer (17% in China; 23% in India),” the study noted.
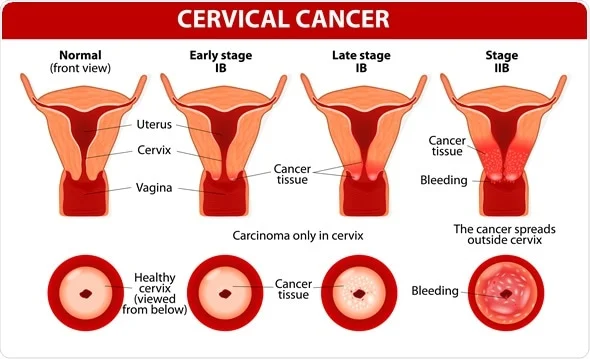
In addition, it noted that in 173 of 185 nations, the age-standardized incidence of cervical cancer in 2020 exceeded the benchmark established by the WHO’s Cervical Cancer Elimination Initiative.
The study also found that there was a distinct and significant socioeconomic gradient between the incidence and mortality rates of cervical cancer and the mean national HDI values, with progressively lower rates seen as HDI grew.
However, the rapid decline in incidence seen in some nations, including India, Thailand, Brazil, and Poland, could be attributed to several number of factors, the survey suggests. These include declines in fertility rates and lower parity, which are declining across successive generations of women, or improvement in the coverage of screening programs and access to treatment services, particularly in the urban population of the registry catchment areas.
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women worldwide, affecting an expected 6,04,000 new cases and 3,42,000 deaths in 2020, with the Region accounting for 32% and 34%, respectively.
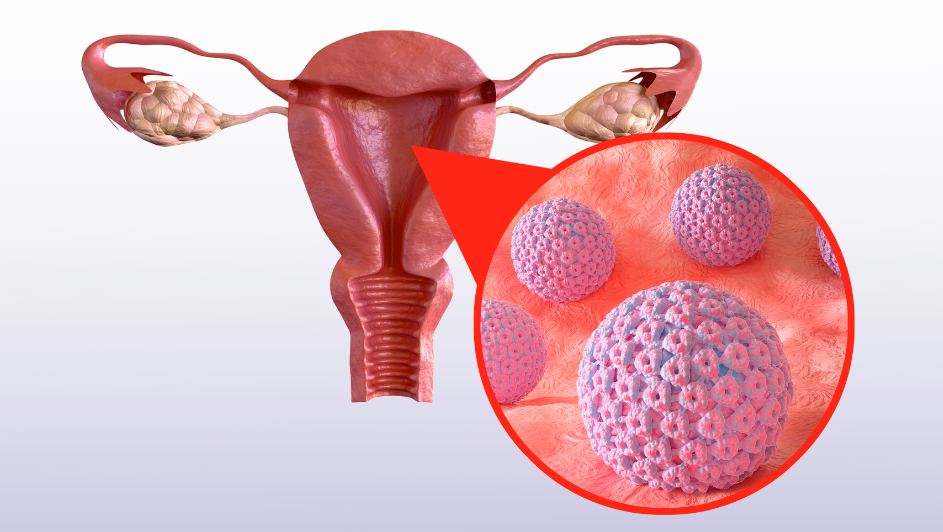
HPV associated with cervical cancer
HPV is the most common viral infection of the reproductive tract. The majority of sexually active women and men will contract the disease at some point in their life, and some may contract it more than once. Over 90% of affected people eventually recover from the virus.
A long-lasting HPV infection that puts a woman at risk for cervical cancer develops in 10% of women with an HPV infection on their cervix. Similar to this, precancers can develop when high-risk HPV remains and infects the cells of the vulva, vagina, penis, or anus.
Nearly 50% of high grade cervical pre-cancers are caused by two human papillomavirus (HPV) types (16 and 18).
HPV is mostly transmitted through sexual contact, and the majority of people become infected with HPV shortly after beginning sexual activity. Over 90% of them eventually get rid of the virus.
Cervical cancer is known to be associated with specific oncogenic (high-risk) HPV strains. A number of cofactors and molecular events affect whether cervical cancer will develop, even though HPV is necessary for the transformation of cervical epithelial cells.
All women are at risk for HPV infections becoming chronic and pre-cancerous lesions developing into invasive cervical cancer, even though the majority of HPV infections and pre-cancerous lesions resolve spontaneously.
In women with healthy immune systems, cervical cancer takes 15 to 20 years to develop. In women with compromised immune systems, such as those with untreated HIV infection, it can happen in just 5 to 10 years.
According to the news agency ANI, the World Health Organization (WHO) has previously stated that India would soon receive human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccinations in an effort to eradicate cervical cancer as a public health issue.
To prevent cervical cancer, HPV vaccination programs have been made available nationally in Bhutan, the Maldives, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
Cervical cancer is treatable if detected early, according to Dr. NK Arora, head of the National Technical Advisory Group on Immunization (NTAGI).
After the age of 35, screening for cervical cancer is crucial, and it should be seen as a mission since “India has the largest burden of deaths due to cervical cancer,” he continued.
Visit website: www.medicalupdates.in

